[NestJS]- NestJs Guards
Guards
Guards@Injectable() 데코레이터 주석이 달리고 CanActivate 인터페이스를 구현하는 클래스다.
NestJS의 Guard는 특정 상황(Permission, Roles, 등)에 따라서 주어진 요청이 라우트 핸들러에 의해서 처리 될지 말지를 결정하는 역할을 한다. 즉 Controller단에 도달하기 이전에 Guards를 거쳐가도록 되어있다.
Guard는 모든 MiddleWare 다음에 실행되고, Interceptor나 Pipe 이전에 실행되기 때문에 Authorization을 구현하는데 많이 사용되며, 권한에 따른 접근 가능한 기능이 분리 되어있을때 이를 구현하기 위해 많이 사용하며, Guard를 사용하여 요청을 처리하기 이전에 안전한 요청인지 파악하여 사전에 차단함으로써, 보안을 위해서 필수적으로 구현 해야하는 사용자 인증이나, 접근제어를 구현하는데 알맞다.
NestJS의 Guard는 Express.js의 MiddleWare와 비슷한 작업을 수행한다고 한다.
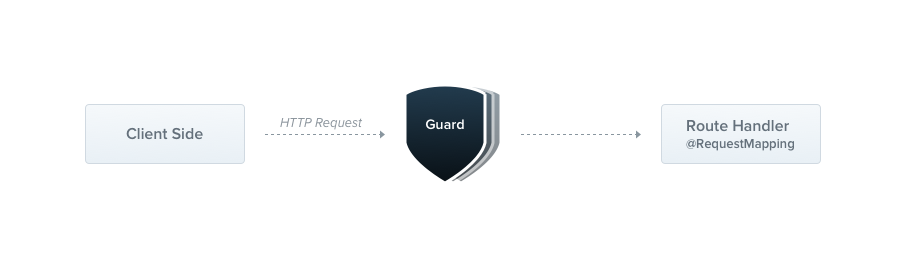 출처:https://docs.nestjs.com/guards
출처:https://docs.nestjs.com/guards
Guard 생성법
@nestjs/common 모듈에서 제공하는 CanActivate 인터페이스를 구현하는 클래스를 생성하고 canActivate() 메서드를 구현해야한다. 아래는 간단하게 모든 요청을 true로 반환하는 예제이다.
import { Injectable, CanActivate } from "@nestjs/common";
@Injectable()
export class AuthGuard implements CanActivate {
canActivate() {
console.log("Auth Success");
return true;
}
}
Execution Context
canActivate() 메서드는 단일 인수인 ExcutionContext 인스턴스를 받아 사용한다. ExcutionContext는 ArgumentsHost 클래스를 상속받는데, 인수를 검색하기 위한 메서드를 제공하여 요청 경로, 요청 헤더, 요청 쿼리, 요청 바디 등을 읽어올 수 있다.
사용 예시는 마지막에 예시 코드와 함께 이해하면 좋을거같다.
Binding Guards
Guard는 Controller-scoped, Method-scoped, Global-scoped 로 지정해줄 수 있다.
Controller-scoped 에서의 적용은 @nestjs/common 모듈의 @UseGuards 데코레이터를 사용하여 적용해줄 수 있다. 아래와 같이 적용하면 이 Controller의 모든 Handler에 Guard가 적용이 되며, 만약 단일 메서드에만 적용을 하기 위해서는 메서드에 @UseGuards 데코레이터를 적용해주면 된다.
@Controller("member")
@UseGuards(AuthGuard)
export class MemberController {}
Global-scoped 에서의 적용은 메인 파일 Nest Application 인스턴스의 UseGlobalGuard() 메소드를 사용하여 적용하면 된다.
const app = await NestFactory.create(AppModule);
app.useGlobalGuards(new AuthGuard());
Gurad 예시 코드
Bearer 토큰을 사용하여 간단한 토큰 기반 인증 예시 코드이다.
Bearer 토큰은 OAuth 2.0에서 주로 사용되는 토큰 유형이며. Bearer 토큰을 사용하면 클라이언트는 서버로부터 받은 토큰을 “Bearer {token}” 형식의 Authorization 헤더에 포함시켜 요청을 보내며, 서버는 이 토큰을 검증하여 클라이언트의 인증 및 권한을 확인하는 방식이다.
Authorization: <type> <credentials>
import {
Injectable,
CanActivate,
ExecutionContext,
BadRequestException,
} from "@nestjs/common";
@Injectable()
export class AuthGuard implements CanActivate {
canActivate(context: ExecutionContext) {
const request = context.switchToHttp().getRequest();
const authorization = request.headers.authorization;
console.log(authorization);
f (authorization) {
const [scheme, token] = authorization.split(" ");
console.log([scheme, token]);
if (scheme.toLowerCase() === "customtoken" && token === "your_secure_token") {
return true;
}
}
hrow new UnauthorizedException('Invalid authorization token');
}
}